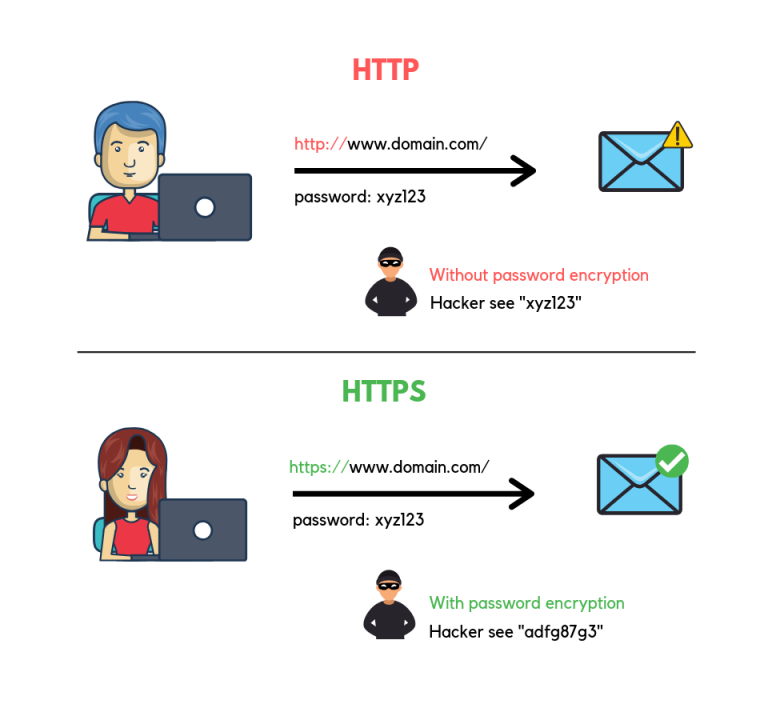
The difference between HTTP and HTTPS is the SSL certificate. A website that loads on HTTPS uses an SSL certificate to send and receive the information in an encrypted state. While on HTTP, the data is sent in text format, which is easy to read by anyone. HTTPS also improves the SEO of the site.
By using HTTPS on your site, instead of HTTP, you take a big step to secure the data on the site. Without installing the SSL certificate, the site is an easy target for Data Theft.
With the Google update, where Google said that it will give a push to the ranking of the sites that use HTTPS, the need for using HTTPS has become more prominent.
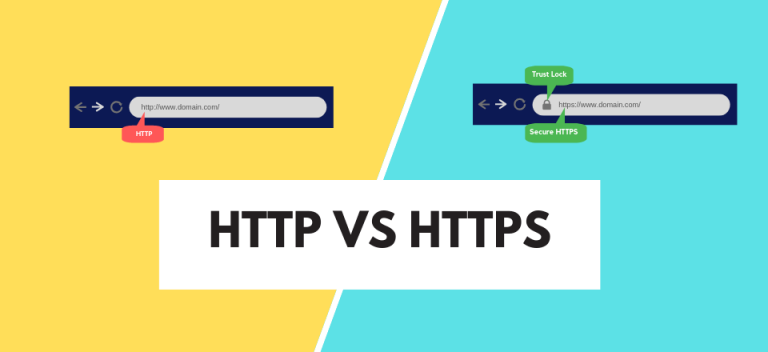
Difference between HTTP and HTTPS
The difference between HTTP and HTTPS is that HTTPS encrypts the data it transmits, while HTTP doesn’t.
So how does HTTPS encrypt Data, but why does HTTPn’t?
We will understand this step by step:
- How HTTP Works?
- How HTTPS Works?
- HTTP vs HTTPS – Detailed
How HTTP Works?
HTTP or HyperText Transfer Protocol provides several protocols for clients (browsers, servers, apps, software) and hosts (servers).
These protocols instruct how to access the information, transfer it, display it, and what action should be initiated when a certain command arrives.
The first documented version of HTTP is V0.9. Created and developed by Tim Berners and his Team at CERN, HTTP was widely accepted by developers. With time, HTTP has been updated and improved a lot, but the method is still the same request-response model.
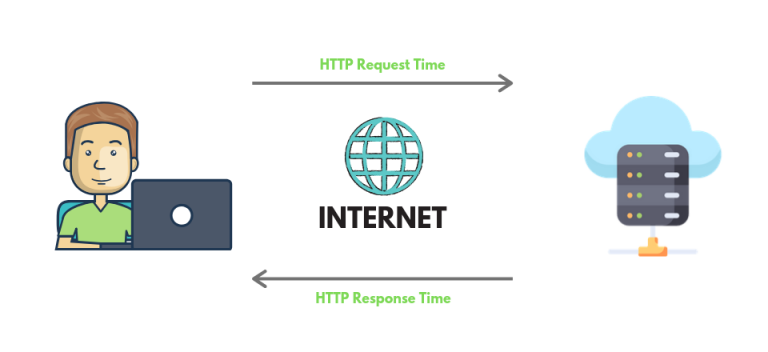
Before anything, there are three important things you need to know:
Connections are not Permanent
The Client and the Server never remain in connections. The client sends the request, and then the connection breaks. To send a response, the server has to re-establish a connection with the client.
In this way, the Client and the Server never remain in a connection when they are not sending data.
Sharing Data Every Time
The Client and Server know each other only during the connection. After the connection ends, they have to start sharing the information from the beginning when the new connection is established.
Every new connection acts like it is the first connection between the server and the host.
Can deliver any Data
Any type of data could be delivered via HTTP, as long as both the Agent and Server can read it.
In the beginning, only text-based data could be fetched, but there are lots of improvements and updates, and now HTTP can deliver any form of data.
How HTTP Fetches the Information?
When you put a URL in the browser, the browser sends the request to the server to fetch the content the URL is directing to.
The request is sent through the Proxies. Proxies are the medium through which the request is sent.
In response, the Server sends the responses as per the Request.
HTTP Request:

This is the request sent by the Client.
- Request Methods
In the request Line, there could be 9 methods:
GET, DELETE, HEAD, POST, TRACE, OPTIONS, CONNECT, PUT and PATCH.
These methods are the commands that tell the server what to do.
- Address of Content
The second part of the request Line is the Address of the Content.
This is the address of the content for which the command has been made.
- HTTP Version
Finally, the HTTP version is specified.
Other than all this stuff, various information is also included in the request. Like the language of the information, the format, and the information of the agent.
All of this information comes to the Server. Then the Server reads it and delivers its response.
HTTP Response:
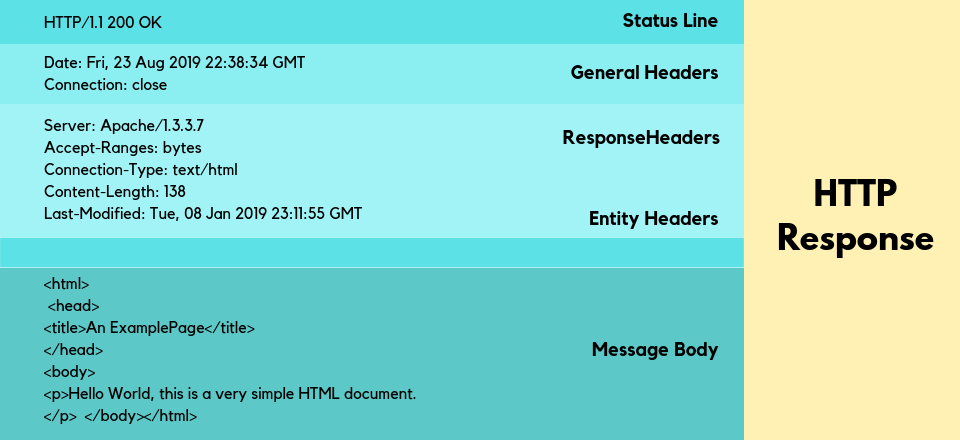
In the first line, the response tells the HTTP version and sends the status code. There are various status codes, and all mean different errors.
- 200 means Okay
- 404 means Not Found
- 502 means Server Errors.
The server also sends other bits of information regarding the content.
Now see an example:
HTTP Request:
GET / HTTP/1.1
Host: www.example.comHTTP Response:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Date: Fri, 23 Aug 2019 22:38:34 GMT
Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
Content-Length: 138
Last-Modified: Tue, 08 Jan 2019 23:11:55 GMT
Server: Apache/1.3.3.7 (Unix) (Red-Hat/Linux)
Accept-Ranges: bytes
Connection: close
<HTML Body>So, now you know how HTTP is responsible for transferring the information from the web server to the browser.
What is HTTPS?
HTTPS was created by Netscape in order to make browsing more secure.
While SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) has been updated to TLS (Transport Layer Security), the web community uses TLS and SSL so interchangeably that they have become synonymous terms.
TLS helps in making the HTTP Request-Response Cycle secure by encrypting the messages of the Request and Response.
Without the TLS, any middleman can read the data, as HTTP send the messages in Plain Text.
The data that has to be transferred between Clients and the Server is wrapped in an encrypted security layer. Only the recipient has the keys to decrypt that layer to access the data and read it. For a middleman, it is just a long string of random characters.
How TLS Encrypts the Data?
Encryption of data is done by using the Public Key, which is decrypted by the Recipients. The Public Key is made available by the server and is present in the SSL certificate.
These certificates are signed by the Certificate Authority. After the Data is encrypted and received, the browser validates the authority of the certificates. Each browser has a list of CAs it trusts.
After showing the certificates, both the Recipient and the Server do the TLS handshake and agree to encrypt the data in a specific way that only both sides can read.
The best part of HTTPS is that at any level, if any person captures your data in the middle, the fetched data will be useless to them.
HTTPS makes the web a secure place to browse.
Difference between HTTP and HTTPS
Now you know how HTTPS works. We see that the functions of HTTP and HTTPS are quite the same. But HTTPS is more secure because of its encryption technique.
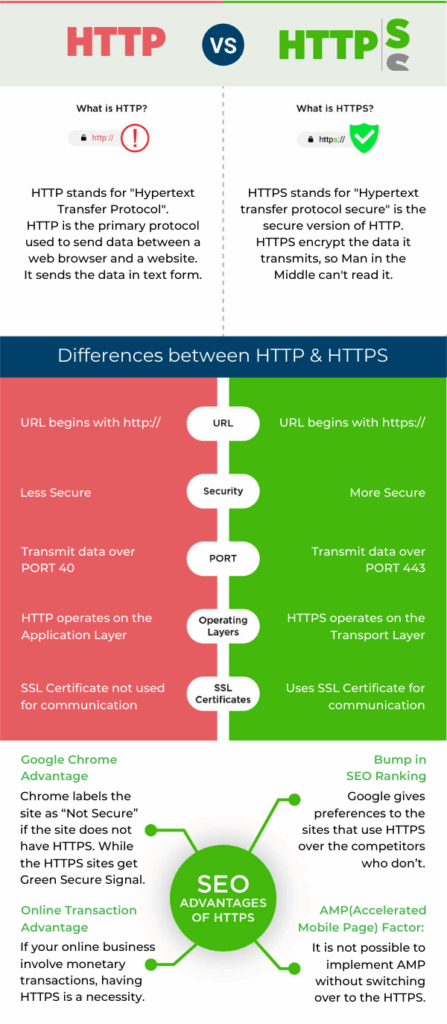
The difference between HTTP and HTTPS is:
- HTTP URL is http:// while the HTTPS URL is https://
- HTTP is not secured, while HTTPS load the page on secure sockets.
- HTTP transmits data over Port 80, while HTTPS works on Port 443.
- HTTP operates on the application layer, while HTTPS operates at the transport layer.
- HTTP does not need an SSL certificate, but HTTPS does.
- HTTP does not improve the SEO of the site, but HTTPS is a ranking factor.
- HTTPS is a necessity in online transactions.
URL is Different
The difference could be seen in the address bar.
The HTTPS before the URL is an indication of a secure site. Without it, the URL load nacked, without a prefix.
Security
HTTP is not secure, and the data could be read by any person who can get their hands on the data. HTTPS encrypts data that only the recipient can open.
Different PORT
HTTP transmits data over PORT 80, while HTTPS does it over PORT 443.
When Tim Berners-Lee issued the documentation of the first version of HTTP, he stated:
“If the port number is not specified, 80 is always assumed for HTTP.”
When the RFC 1340 was released, the IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force) assigned Port 80 to HTTP.
When the new RFC arrived in the year 1994, HTTPS appeared for the first time in the document and was assigned port 443.
The reason they chose these ports was that they were available at the time.
Operating Layers
HTTP operates on the Application Layer. On the other hand, HTTPS operates on the Transport Layer.
HTTP works on the notion of making the Data readable for the recipients.
While the Transport Layer is responsible for moving the data from Point A to Point B. So, operating with the Transport Layer, HTTPS enjoy the wrapped security layer.
SSL Certificates
You need to install signed SSL certificates for HTTPS.
SSL certificates are available both Free and Expensively priced. You can choose anyone as your business demands.
HTTP does not need any certificates, as it does not decrypt anything and sends everything in Plain Text.

SEO Advantages
If the security measures the HTTPS provides failed in enticing you to switch over to HTTPS, maybe the SEO advantages would do:
Bump in Ranking
Google gives preferences to the sites that use HTTPS over the competitors who don’t.
If you don’t switch, your competitor may take your position.
Google Chrome
Google Chrome is one of the most popular browsers. Chrome labels the site as “Not Secure” if the site does not have HTTPS.
That is a red flag for any potential customer.
While the HTTPS sites get a Green Secure Signal.

Online Transactions
If your online business involves monetary transactions, it becomes very important to have HTTPS. 84% would abandon the purchase if they see the connection is not secure.
And User Behaviour is one of the major ranking factors, after the RankBrain update.
AMP Factor
It is not possible to implement AMP without switching over to HTTPS.
With more and more searches coming from mobile, and Google prioritising the mobile-first sites, it is important to keep the doors open.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between HTTP and HTTPS
The main difference between HTTP and HTTPS is security. HTTP is not secure, and HTTPS use TLS to encrypt the data and secure the connection.
Which is better, HTTP or HTTPS?
Between HTTP and HTTPS, HTTPS is a better option. It improves trust and helps in SEO, too.
Is HTTPS faster than HTTP?
Well, it is complicated. Initially, there area few connections HTTPS has to make the connection secure before actually transmitting the Data. It takes a little bit of time. But HTTP/2 is fast.
Gradually, more and more sites will update to HTTP/2.
Why is HTTPS more secure than HTTP?
HTTPS is more secure than HTTP because it delivers the information in an encrypted form. That encryption can only be opened by the recipients.
That’s why it is safe from Man in the Middle Attack and Hijack Attacks.
How do I redirect HTTP to HTTPS?
There are various ways to redirect HTTP to HTTPS.
Summary
HTTPS helps in building the Trust. Building trust in business is important for running a long-term business.
As you know, the Internet does have an image of being an unsafe environment, so a site should do anything and everything to become secure.
HTTPS is one major way to become safe.
It is better to switch to HTTPS than to keep using HTTP and become a victim of any unfortunate events.
We hope this article will help you to grasp the conceptual difference between HTTP and HTTPS.
If the doubts remain, leave your query in the comments.




